External rotor motors, also known as outrunner motors, are a crucial component in various industries, ranging from aerospace to automotive and manufacturing. Ensuring the quality and performance of these motors is paramount to their successful operation. This article will delve into the quality requirements outlined by international standards and discuss the inspection process to verify compliance.

Contents
Quality Requirements
1. Material Selection
The first and foremost quality requirement for external rotor motors is the selection of high-quality materials. The rotor, stator, and other components must be constructed from materials known for their durability, heat resistance, and electrical conductivity. Common materials include high-grade steel for the rotor and stator, copper for windings, and specialized alloys for bearings.
2. Manufacturing Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing is crucial for the proper functioning of external rotor motors. International standards stipulate specific tolerances for critical dimensions such as rotor and stator air gaps, winding clearances, and bearing fits. These tolerances ensure that the motor operates within specified efficiency and performance ranges.
3. Insulation Systems
The insulation system of an external rotor motor is designed to withstand the electrical stresses encountered during operation. It must be capable of preventing electrical breakdowns and ensuring a long service life. Quality requirements mandate the use of high-grade insulation materials, such as Class F or H insulation, which can handle elevated temperatures without degradation.
4. Thermal Management
Efficient thermal management is essential for preventing overheating and subsequent damage to the motor. Quality external rotor motors are equipped with effective cooling mechanisms, such as fans or liquid cooling systems. Additionally, the design must allow for proper heat dissipation to ensure the motor’s longevity and reliability.
International Standards
To establish a universal benchmark for quality and performance, external rotor motors are subject to various international standards. The two most prominent organizations that set these standards are the IEC and NEMA.
1. IEC Standards
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is a global body responsible for developing and publishing international standards for all electrical, electronic, and related technologies. For external rotor motors, the IEC has established several standards that cover aspects such as dimensions, performance, efficiency, and safety.
IEC 60034-2: Rotating Electrical Machines – Part 2: Methods for Determining Losses and Efficiency of Rotating Electrical Machinery from Tests
This standard provides methods for determining the losses and efficiency of rotating electrical machinery, including external rotor motors. It outlines test procedures and calculations to assess the motor’s overall performance.
IEC 60034-30: Rotating Electrical Machines – Part 30: Efficiency Classes of Single-Speed, Three-Phase, Cage-Induction Motors (IE Code)
This standard classifies the efficiency of single-speed, three-phase cage-induction motors, including external rotor motors. It establishes different efficiency classes, allowing manufacturers and users to select motors based on their energy efficiency requirements.
2. NEMA Standards
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) is a North American organization that sets standards for electrical equipment and systems. While primarily focused on the North American market, NEMA standards are recognized and used worldwide.
NEMA MG 1-2018: Motors and Generators
This standard covers the general requirements for motors and generators, including external rotor motors. It addresses design, performance, testing, and other critical aspects to ensure the quality and reliability of electrical machines.
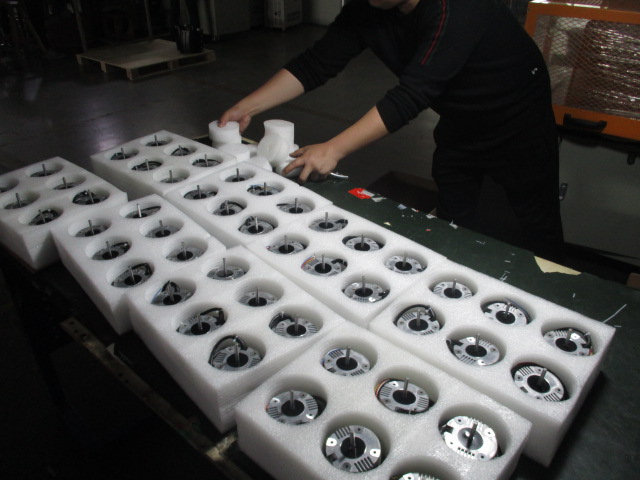
Inspection Process of External Rotor Motors
NBNQC is a crucial step in verifying the compliance of external rotor motors with international standards and quality requirements. It involves a systematic assessment of various aspects of the motor’s design, construction, and performance. The process can be summarized in the following steps:
1. Documentation Review
The inspection begins with a thorough review of all relevant documentation, including engineering drawings, material specifications, test reports, and certificates. This step ensures that the motor has been designed and manufactured in accordance with the specified standards and requirements.
2. Visual Inspection
A visual inspection is conducted to assess the overall quality of the motor’s construction. Inspectors check for any signs of physical damage, irregularities in machining or assembly, and adherence to dimensional tolerances.
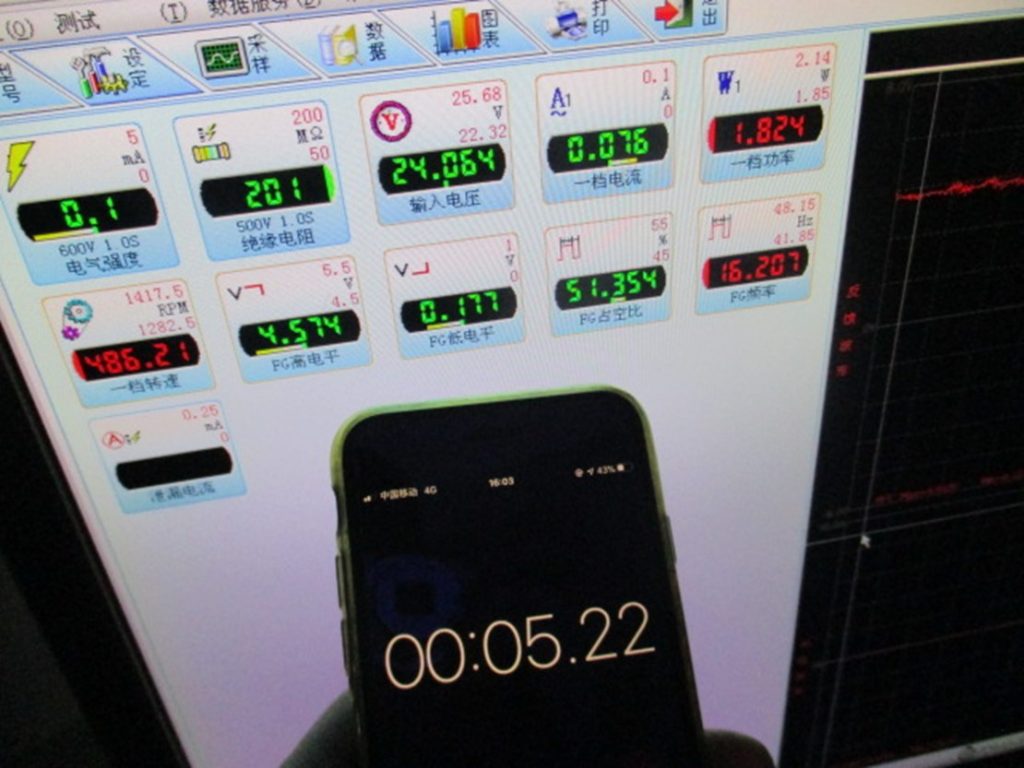
3. Electrical Testing
Electrical tests are performed to evaluate the motor’s electrical properties. This includes measurements of resistance, insulation resistance, and inductance. These tests confirm that the motor’s electrical components and insulation systems meet the specified standards.
4. Performance Testing
Performance testing involves running the motor under controlled conditions to assess its operational characteristics. This includes measurements of speed, torque, power output, and efficiency. The results are compared against the performance criteria outlined in the relevant standards.
5. Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis is conducted to ensure that the motor operates within safe temperature limits. This may involve running the motor at full load for an extended period while monitoring temperatures at critical points. The data collected is compared against specified limits.
6. Efficiency Verification
Efficiency testing is performed to confirm that the motor meets the efficiency class requirements as defined by the applicable standards. This is crucial for determining the motor’s energy-saving potential in practical applications.
Conclusion
External rotor motors play a vital role in numerous industries, and ensuring their quality is of paramount importance. Adherence to international standards, such as those established by the IEC and NEMA, provides a reliable framework for manufacturers and users alike. The NBNQC process serves as a critical step in verifying compliance with these standards, guaranteeing that external rotor motors meet the highest quality and performance requirements.
In summary, a combination of meticulous manufacturing practices, adherence to international standards, and rigorous inspection processes ensures that external rotor motors deliver optimal performance, reliability, and longevity in their respective applications.






